There are far ranges of Linux bioinformatics tools available and widely used in this field for a long while. Bioinformatics has been characterized in many ways; however, it is frequently defined as a combination of mathematics, computation, and statistics to analyze biological information. The main goal of the bioinformatics tool is to develop an efficient algorithm so that sequence similarities can be measured accordingly.
Best Bioinformatics Tools for Linux
This article has been written by focusing on the bioinformatics tools available on the Linux platform. All the efficient tools have been discussed and reviewed in detail. Moreover, you will find the essential features, properties, and download links from this article. Hence, let’s go through it.
1. geWorkbench
geWorkbench can be elaborated with genome workbench, a java-based bioinformatics tool for integrated genomics. Its components architectures facilitate specifically developed plug-ins that would be configured into complicated bioinformatics applications. Currently, seventy-plus plugs are available to support, visualize, and analyze sequence data.
Features of geWorkbench
- It is included many computational analysis tools, namely, t-tests, self-organizing maps, hierarchical clustering, and so on.
- It is featured with molecular interaction networks, protein structure, and protein data.
- It offers gene integration and annotation pathways and collects data from curated sources for gene ontology enrichment analysis.
- This tool integrates components with the platform management of inputs and outputs.
2. BioPerl
BioPerl is a collection of Perl tools widely used in the Linux platform as a bioinformatics tool for computational molecular biology. It is continuously used in the bioinformatics fields in a set of standard CPAN-style. This bioinformatics tool is well-documented and freely available in Perl modules. Because of being object-oriented, these modules are interdependent to accomplish the task.
Features of BioPerl
- From the local and isolated databases, this bioinformatics tool access nucleotide and peptide sequence data.
- It manipulates distinct sequences and transforms the form of database and file records.
- It is a bioinformatics search engine that looks for similar sequences, genes, and other structures in genomic DNA.
- By generating and manipulating sequence alignments, it develops machine-readable sequence annotations.
3. UGENE
UGENE is a free open source and a set of integrating bioinformatics tools for Linux. Its common user interface is integrated with mostly used and well-familiar bioinformatics applications. Numerous biological data formats are compatible with their toolkits; thus, data can be retrieved from remote sources. This tool utilizes multicore CPUs and GPUs to provide the maximum possible performance to optimize its computational activities.
Features of UGENE
- Its graphical interface offers several features, for instance, chromatogram visualization, multiple align editor, and visual and interactive genomes.
- It paves the way for a 3D view in PDB and MMDB formats along with anaglyph stereo mode support.
- It facilitates Phylogenetic tree view, Dot plot visualization, and query designer can search for intricate annotation patterns.
- It can pave the way for custom computational workflow for the workflow designer.
4. Biojava
Biojava is an open source and exclusively designed for the project to provide the required java tools to process biological data. It works for far ranges of datasets, for instance, analytical and statistical routines and parsers for common file formats. Moreover, it facilitates the manipulation of sequence and 3D structure. This bioinformatics tool for Linux aims to expedite swift application development for biological datasets.
Features of Biojava
- Including class files and objects, it is a package that implements java code for various datasets.
- Biojava can be used in different projects such as Dazzel, Bioclips, Bioweka, and Genious, which are used for various purposes.
- It works for file parsers along with the DAS clients and server support.
- It is used for making sequence analyses for GUIs and can access BioSQL and Ensembl databases.
5. Biopython
Biophython bioinformatics tool developed by an international team of developers and written in python program is used for biological computation. It offers access to a fair range of bioinformatics file formats, namely, BLAST, Clustalw, FASTA, and Genbank, and allows access to online services such as NCBI and Expasy.

Features of Biopython
- It is accumulated with python modules that work on making a sequence with interactive and integrated nature.
- This bioinformatics tool can perform in different sequences, for instance, translation, transcription, and weight calculations.
- This tool is exclusively enriched; thus, protein structure and sequence format get managed efficiently.
- This tool works for alignments; thus, a standard can be established to create and deal with substitution matrices.
6. InterMine
InterMine is an open-source bioinformatics tool for Linux that works as a data warehouse to integrate and analyze biological data. Being software, users can install it on their device and make data available on the web page. It is believed to be one of the most dynamic data tables that can easily drill down into data and smooth the way of filtering data. What is more additional column to navigate towards the report page?
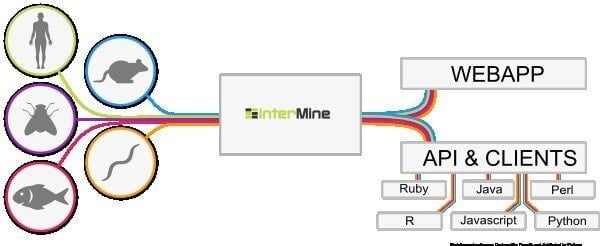
Features of InterMine
- It works with a single object, such as a gene, protein, or binding site, and multiple lists, such as a list of genes or proteins.
- It can be operated in multi-languages; thus, different queries regarding biometrics information can be searched in a couple of languages.
- This software has four search tools: template search, keywords search, query builder, and region search.
- It supports different formats such as Chado, GFF3, FASTA, GO & gene association files, UniProt XML, PSI XML, In Paranoid orthologs, and Ensembl.
7. IGV
IGV, elaborated as an interactive genomics viewer, is believed to be one of the most effective visualization tools that can easily access an extensive and interactive genomics database. It can offer a wide variety of data types with genomic annotation along with array-based and next-generation sequence data. Just like Google Maps, it can navigate through a data set and smooth the way of zooming and panning seamlessly across the genome.
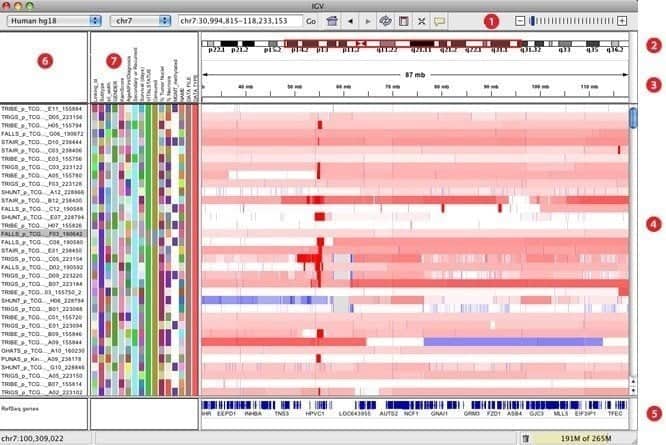
Features of IGV
- It offers flexible integration of far ranges of genomic datasets, including aligned sequence reads, mutations, copy numbers, etc.
- It expedites enabling real-time exploration regarding the massive supportive dataset by using efficient and multi-resolution file formats.
- It allows simultaneous visualization of various data types among hundreds and, to some extent, up to thousands of samples.
- It allows loading datasets from local and remote sources, including cloud data sources, to observe their own and publicly available genomic datasets.
8. GROMACS
GROMACS is a dynamic molecular simulator that is included analysis and building tools. It is a package with versatility and intends to work on molecular dynamics; for instance, it can simulate the Newtonian equation of motion from hundreds to thousands of particles. It was programmed to perform on biochemical molecules at the earlier stage, namely protein and lipids, bonded with complicated interactions.
Features of GROMACS
- This Linux informatics tool is user-friendly, contains topologies and parameter files, and is written in cleartext.
- Script language is not used; thus, all programs are operated with a simple interface command-line option for input and output files.
- If anything goes wrong, many error messages and consistency checking get done.
- All programs are facilitated with an integrated graphical user interface.
9. Taverna Workbench
The Taverna Workbench is an open-source tool programmed to design and execute bioinformatics workflows created by the myGrid project. A range of software can be integrated with this tool, including SOAP and REST web service. It collaborates with distinct organizations such as the European Bioinformatics Institute, the DNA Databank of Japan, the National Center for Biotechnology Information, SoapLab, BioMOBY, and EMBOSS.
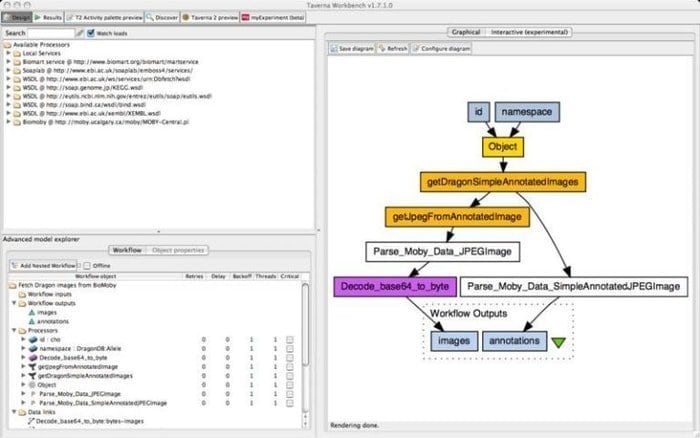
Features of Taverna Workbench
- It is entirely designed with a graphical workflow for finding, developing, and executing workflows.
- It has been designed with an entirely graphical workflow; moreover, discrete tabs are used for design.
- Annotations are given for describing workflows, services, inputs, and outputs with a built-in help facility.
- Previously used workflow is stored in this tool, even if it can save inputs workflow used in the file.
10. EMBOSS
EMBOSS implies European Molecular Biology Open Software Suite. It is a package of software that has been developed for the molecular biology community’s needs. This Linux bioinformatics tool can be used for different purposes. For instance, it is functional in various formats of data automatically. Moreover, it can collect data sequentially from the web page.
Features of EMBOSS
- EMBOSS includes hundreds of applications, namely, sequence alignment and rapid database searching with sequence patterns.
- Additionally, it has protein motif identification, including domain analysis and nucleotide sequence pattern analysis.
- Its toolkit has been designed appropriately to address the bioinformatics application and workflow.
- It has been programmed with additional libraries to handle many other relevant issues as well.
11. Clustal Omega
Clustal Omega works on protein, and RNA/DNA is a multiple sequence alignment program designed for general purposes. It can efficiently handle millions of datasets in a reasonable time; moreover, it produces high-quality MSAs. In this bioinformatics tool, there is a process where the user requires leaving the file sequence in the default mode. That gets aligned and clustered to generate a guide tree, ultimately allowing for a progressive alignment sequence.
Features of Clustal Omega
- It facilitates aligning existing alignments with each other and, what is more, aligning a sequence to an alignment using a hidden Markov Model.
- An external profile alignment feature refers to a new homologous sequence for the hidden Markov Model.
- HMMs are used for the Clustal Omega for the alignment engine taken from the HHalign package from Johannes Soeding.
- Clustal Omega allows three sequence inputs: the profile, align the sequence, and HMM.
Clustal Omega
12. BLAST
Basic Local Alignment Search Tool or BLAST is used for finding the similarity among biological sequences. It can find relevant matches between nucleotide and protein sequences and show their statistical importance of it. Query sequences are structured with different types of BLAST. What is more, this tool is largely cultivated thriving unknown genes in various animals, and it lets mapping out sequence-based datasets through qualitative analysis.
Features of BLAST
- The megaBLAST nucleotide-nucleotide offers to search and optimize for very similar types of sequences.
- Additionally, the BLASTN nucleotide-nucleotide works slightly differently as it looks for distance sequences.
- Moreover, BLASTP finds protein-protein relation and comparison, and its formula is used for other research.
- TBLASTN focuses on the nucleotide query against the protein dataset and can translate the database on the fly.
13. Bedtools
Bedtool bioinformatics software is a Swiss army knife of tools used for far ranges of genomic analysis. Genomic arithmetic uses this tool very widely, which implies it can find the set theory with it. For instance, bedtools facilitate one to count, complement, and shuffle intersect, merge genomic intervals from multiple files, and generate a particular genome format such as BAM, BED, GFF/GTF, and VCF.
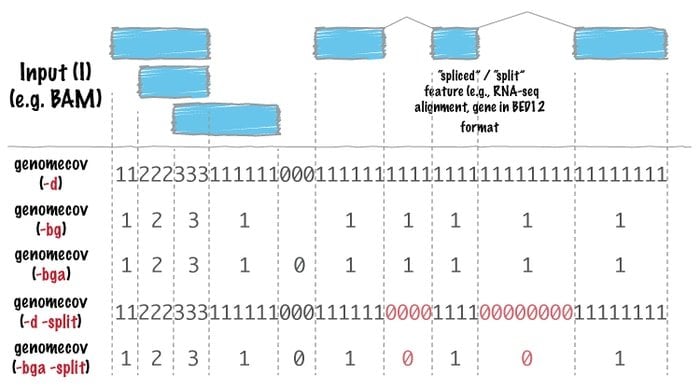
Features of Bedtools
- In this bioinformatics tool, each is designed to perform a particularly simple task, e.g., intersect two interval files.
- The complicated and sophisticated analysis gets done by using a combination of bedtools.
- A group researcher developed this tool in Utah University’s Quinlan laboratory.
- Since this tool has many options, it can be used for multi-purposes in bioinformatics.
14. Bioclipse
Bioclipse Linux bioinformatics tool that is defined with workbench for life science is a java-based open-source software. It works on the visual platform, including chemo and bioinformatics Eclipse Rich Client Platform.
It is featured with a plugin architecture. That implies the state-of-the-art plugin architecture moreover, functionality, and visual interfaces from Eclipse, such as the help system and software updates also included.
Features of Bioclipse
- Biological sequences, namely RNA, DNA, and protein, are managed with the bioclipse.
- Biojava assists in providing core bioinformatics functionality also; graphical editors for sequence alignments as well.
- It is used for pharmacology and drug discovery along with the site of metabolism discovery.
- Finally, it works on semantic web functionality, browsing extensive compound collections and editing chemical structures.
15. Bioconductor
Bioinformatics used extensively in the Linux platform, is an open-source and free bioinformatics tool, coherently used in medical biology for high-throughput analysis. It mainly uses statistic R programming; nevertheless, it also contains another programming language as well. This software is designed by focusing on a couple of objectives; for instance, it aims to establish collaborative development and to use innovative software immensely.
Features of Bioconductor
- This software can analyze a range of data, for instance, oligonucleotide arrays, Sequence analysis, and flow cytometer, and generate a robust graphical and statistical database.
- Having vignettes and documents in each Binocular package can provide a textually and task-oriented description of that package’s functionality.
- It can generate real-time data regarding the associating microarray and other genomic data along with biological metadata.
- Additionally, it can analyze expressed genes such as LIMMA, cDNA Arrays, Affy Arrays, RankProd, SAM, R/maanova, Digital Gene Expression, and so on.
16. AMPHORA
AMPHORA, which stands for Automated Phylogenomic infeRence Application, is an open-source bioinformatics workflow tool. Another AMPHORA version, AMPHORA2, has bacterial and 104 archaeal phylogenetic marker genes. More importantly, it works to create information between phylogenetic and met genetic datasets.
Features of AMPHORA
- Because of being single genes, AMPHORA2 is the most suitable for deducing the taxonomic composition of bacteria.
- Moreover, it also can infer the taxonomic composition of archaeal communities from the metagenomic shotgun sequence.
- Initially, AMPHORA was used to analyze the Sargasso Sea metagenomic data.
- However, nowadays, AMPHORA2 is increasingly used to analyze relevant metagenomic data in this regard.
17. Anduril
Anduril is open source components-based bioinformatics software for Linux that works to create a workflow framework regarding scientific data analysis. The Systems Biology Laboratory, University of Helsinki, develop this tool. This bioinformatics tool for Linux is designed to enable efficient, flexible, and systematic data analysis, particularly in the biomedical research field.
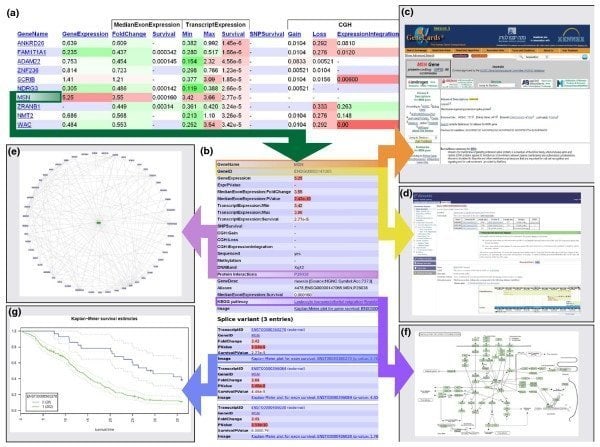
Features of Abduril
- It works in a workflow where different processing system is interrelated; for instance, an output of a process can work as an input of others.
- The primary Anduril tool is written in Java, whereas other components are written in different applications.
- In its various steps, numerous activities occur, such as creating data, generating reports, and importing data.
- Its workflow configuration can be done with a simple overtness, powerful scripting language, namely, Andurilscript.
Get Anduril
18. LabKey Server
LabKey Server is a preferred choice for the scientists used in the laboratories to integrate research, analyze and share biomedical data. A secure data repository is used in this tool that facilitates web-based querying, reporting, and collaborating within a far range of databases. Along with the underlying platform, many more scientific instruments can be added to this application.
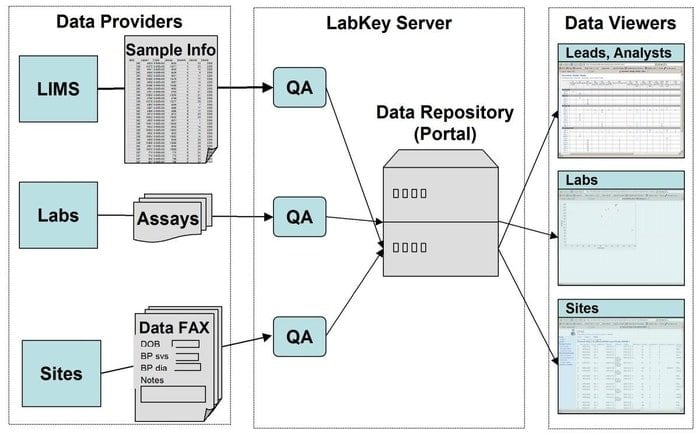
Features of LabKey Server
- LabKey Server is featured with all types of biomedical data. For instance, flow cytometry, microarray, mass spectrometry, microplate, ELISpot, ELISA, etc.
- In this tool, a customizable data processing pipeline executes all the relevant activities.
- It is featured with observational studies that support the management of longitudinal, large-scale studies of participants.
- Proteomics is used for processing high-throughput mass spectrometry data using a specific tool, namely, X! Tandem.
19. Mothur
Mothur is an open-source bioinformatics tool widely used in the biomedical field for processing biological data. It is a software package frequently used for analyzing DNA from uncultured microbes. Mothur is a Linux bioinformatics tool that can process data generated from DNA sequence methods, including 454 pyro-sequencing.
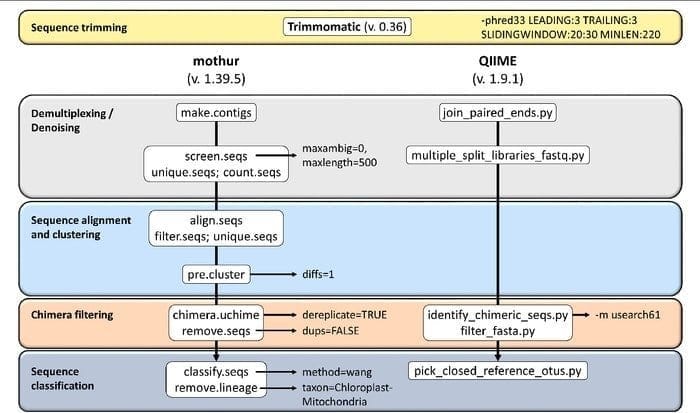
Features of Mothur
- It is a single-package software capable of handling community data analyzing and making a sequence.
- Large-scale community documentation support and another form of support are provided with this tool.
- It is believed Mothur is the most prominent bioinformatics tool for analyzing 16S rRNA gene sequences.
- A dedicated community and tutorials are available in this tool to inform how to use Sanger, PacBio, IonTorrent, 454, and Illumina (MiSeq/HiSeq).
20. VOTCA
VOTCA stands for Versatile Object-oriented Toolkit for Coarse-graining Applications, which is branded as an efficient bioinformatics tool with a Coarse-grained modeling package that mainly analyzes molecular biological data. It aims to develop systematic coarse-graining techniques and simulate microscopic charges to transport disordered semiconductors.
Features of VOTCA
- VOTCA is mainly featured with three major parts: the Coarse-graining toolkit, the Charge Transport toolkit, and the Excitation Transport Toolkit.
- All three core features are from the VOTCA tool library that implements shared procedures.
- VOTCA uses coarse-graining methods to harvest the best outcomes from relevant activities.
- This software features an excitation transport toolkit where orca DFT packages are supported significantly.
Final Thought
To encapsulate the whole thing, it is worth mentioning here that all the forth mentioned bioinformatics applications are extensively used in this field. These Linux bioinformatics tools have been used in medical science, pharmacology, drug invention, and relevant sphere for a long while.
Finally, you are requested to leave your two pennies regarding this article. What is more, if you find this article worthwhile, please do not forget to like, share, and comment. Your precious comment will be appreciated.


