Linux Task Manager is one of the essential tools that help you to find out the details of resource usage (CPU/RAM) by any particular software or even the system itself. There are lots of software you need to run on your system, and sometimes you find that some are causing the problem or freezing the system by taking excessive resources. In those instances, you need a Linux task manager to identify or stop that process and program.
Best Linux Task Managers
There are tons of Linux task managers available in the market. Moreover, every Linux distribution has a distro-specific task manager depending on various Linux desktop environments. Some are GUI-based, and some are CLI-based. But which one will you use as a kill switch to stop problematic applications or measure system performance?
In this article, I will show you a generic list of the best Linux task managers covering both CLI and GUI based. I firmly believe this task management program will help you to manage your Linux system smoothly.
CLI-based Linux Task Manager
As a Linux lover, I always use a command-line interfaced program. I believe you also do so. Moreover, if you are a server admin where GUI is absent, this CLI-based Linux task manager will be an excellent help for performing some specific tasks. Now, let’s get started with our list.
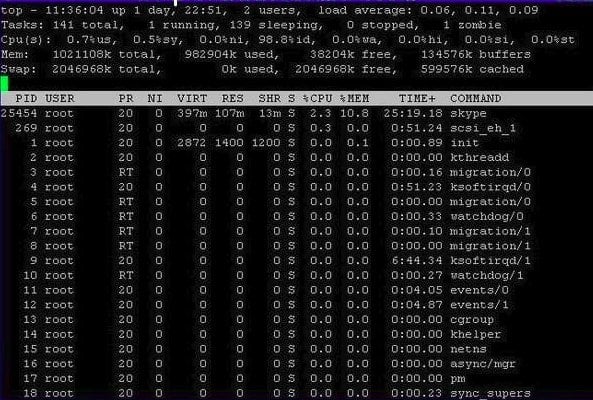
1. Top
“top” is one of the best Linux task managers available. You can use this task management tool in every Linux distro by using the Terminal. As a Linux system administrator, by using the “top” tool, you get various important information about your system, like the total no of running processes, CPU usage, SWAP usage, free and used RAM resources, etc.
2. Glances – A Eye of Your System
“Glances” is one of the best Linux system monitoring tools based on Python and open architecture, where developers can add various custom plugins to increase its functionality and flexibility.
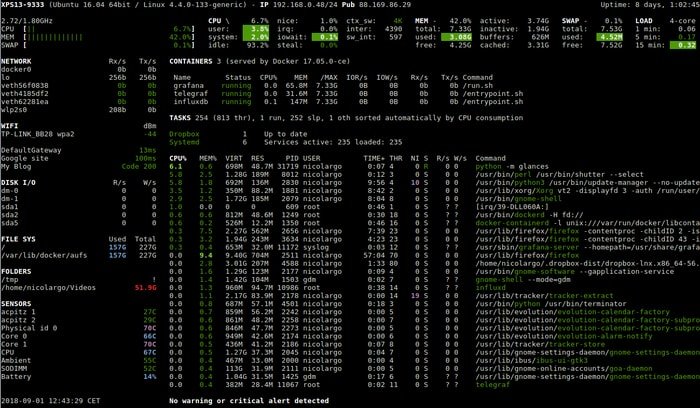
It’s a cross-platform resource monitoring tool that helps you grab a large amount of data for your system resources through the web interface or curses. It also works in client and server mode, where remote monitoring can be achieved via the web interface, terminal, or API (XML-RPC and RESTful).
3. Htop
Htop is an interactive process viewer and text-based task manager for the Unix system. This tool offers many useful options to the system admin, such as stopping, restarting, and controlling the programs.
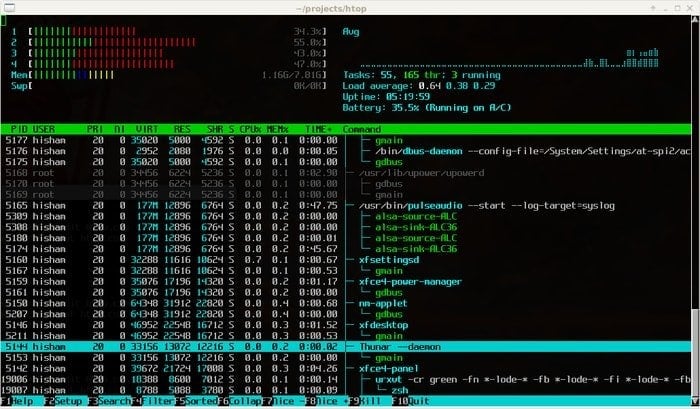
It also provides a handful of information about your system, including memory and CPU consumption. It’s a modern, easy-to-use, and responsive Linux task manager as Htop is text-based so that it can be run anywhere, even over the internet, on a server via SSH.
4. Ps
Though Ps is not a complete task manager but still a useful barebones command-line system monitoring tool that helps you show various running programs, it’s a scriptable tool that runs and works well in collaboration with other commands terminal, which is effective and useful for any system admin.
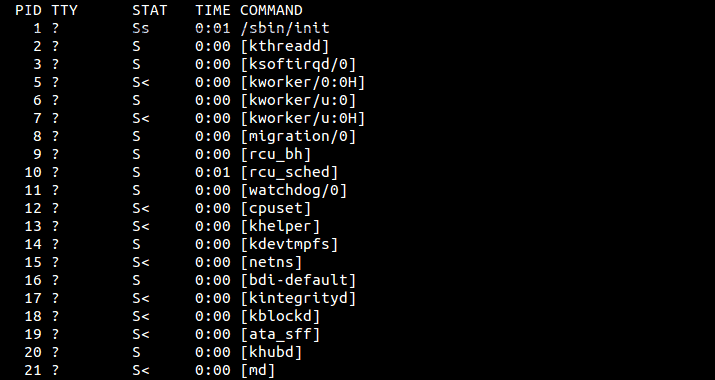
The user does not need to install it in the system as it comes prepacked with every Linux distro. Ps has some handy command arguments that help sort the processes and IDs.
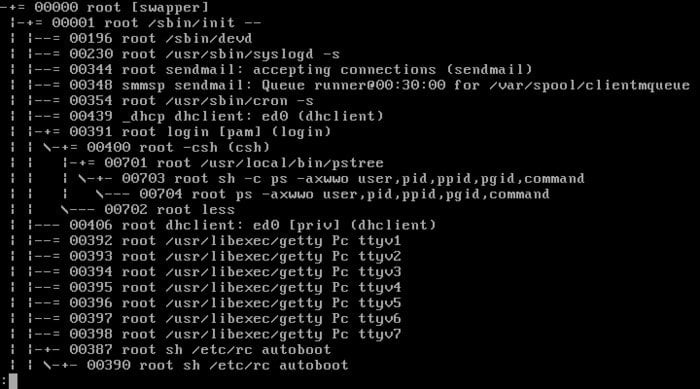
5. Pstree
Pstree is a Linux command and visual alternative to the ps command, which shows the system running threads and processes as a “tree.” It shows all process trees rooted in processes owned by a user-specified beforehand.
GUI-Based Linux Task Manager
Now I will show you some of the best GUI-based Linux task managers, which will help the new user understand the system engagement with various threads and processes and ultimately helps to control the Linux applications.
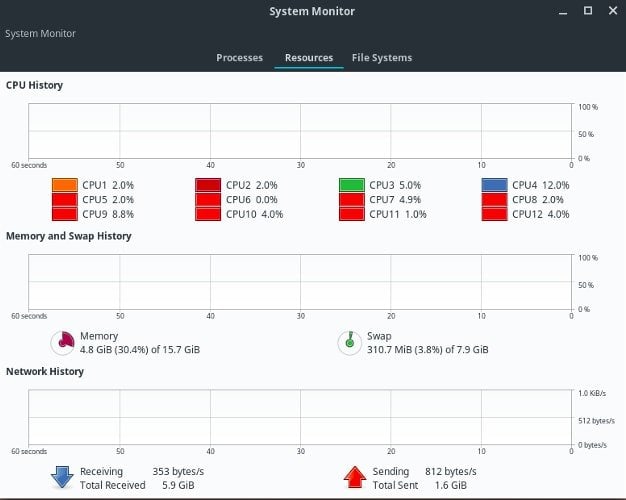
6. Gnome System Monitor
Gnome system monitor is a lightweight and minimalistic but powerful Linux task manager for the Gnome shell desktop environment. This Linux system monitoring tool shows you various important information about hard drive space, RAM/SWAP usage, running process and time, network activity, etc., in an easily understandable display.
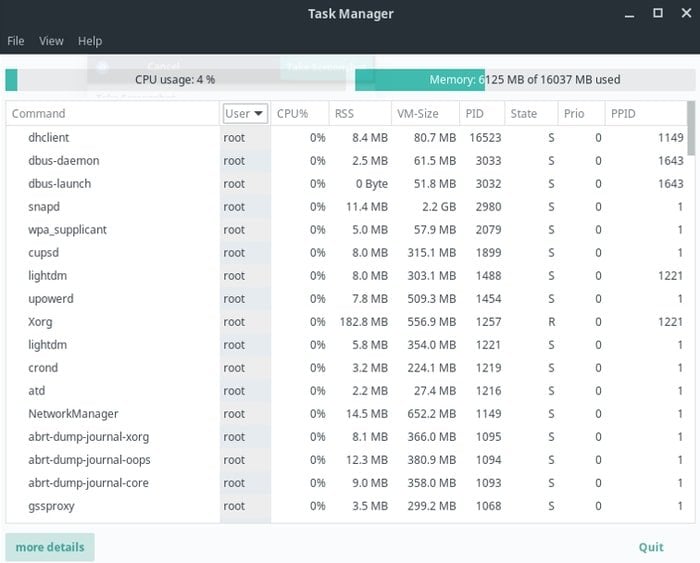
7. LXTask
Like the Gnome system monitor, LXTask is a lightweight and minimalistic Linux task manager for the LXDE/LXQt desktop environment. It’s based on the GTK+ toolkit and doesn’t take many resources to run on any system while helping you sort out the problematic applications. LXtask helps users perform specific root tasks and display a table of information about any running process.
8. Stacer
Stacer is an interactive and modern GUI-based Linux system optimizer and monitoring software. This Linux task manager has been developed to focus on beginner Linux users. It’s a combo package that includes a Linux task manager, software package manager, system optimizer, resource viewer, system cleaner, etc.
9. Mate System Monitor
The mate system monitor is a default system monitoring software for the MATE desktop environment. It’s a GUI-based Linux Monitoring tool that is helpful for newbie Linux users to get some vital information regarding the system.
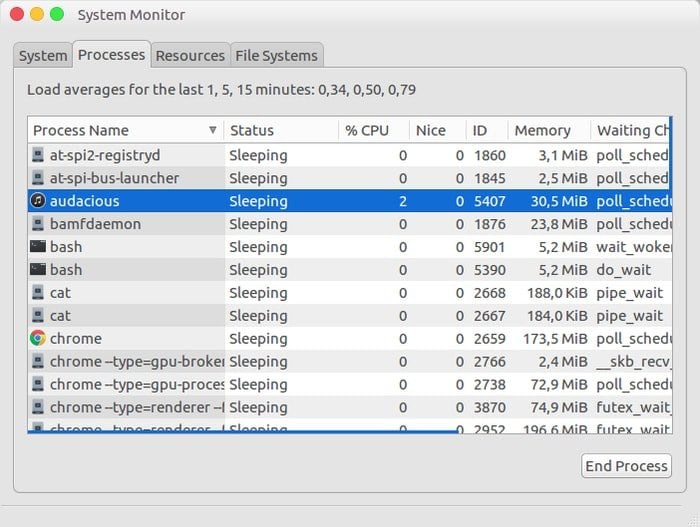
Mate system monitor lets you know the total running processes with IDs, memory and CPU usage, and much more through the intuitive “tab” interface. Moreover, It provides some advanced functionality for killing, stopping, or changing the priority of various processes as you wish.
10. KSysGuard
KSysGuard is the default Linux task and system performance monitor for the KDE desktop environment. One of the notable features of this Linux task manager is it supports client/server architecture that lets you monitor both remotely and locally.
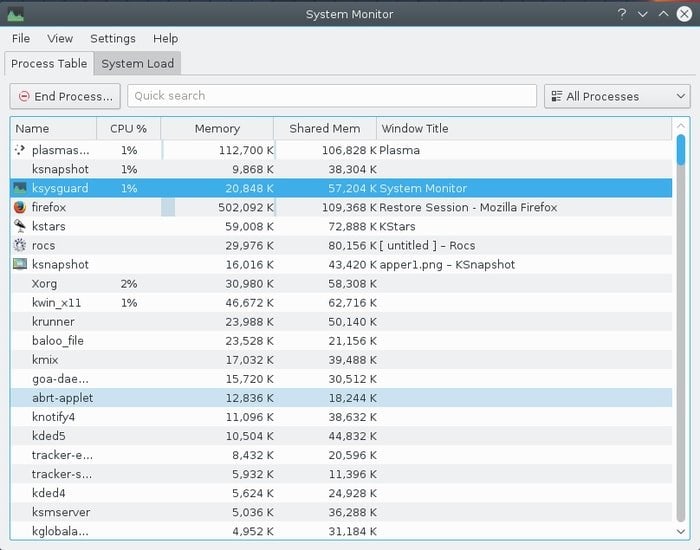
It’s called a no-nonsense task manager, allowing you to kill/end the problematic program easily. KSysGuard can be used both from the graphical interface and Terminal mode.
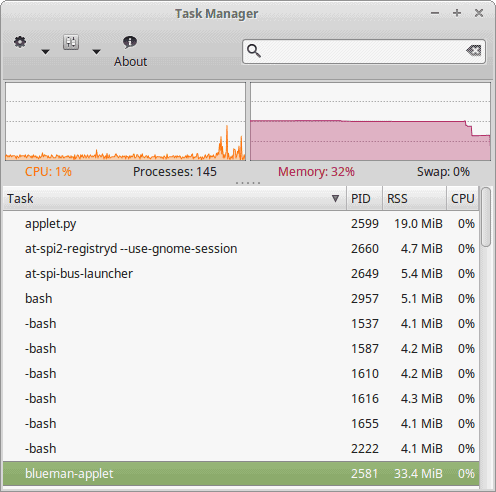
11. XFCE4 Task Manager
XFCE Task Manager is another default Linux task manager for the XFCE desktop environment. Like LXTask, this tool is also very lightweight and well-integrated with the system. Like any other Linux task manager, it also helps you get system information like CPU and memory usage, running processes with IDs, etc. You get a handful of options when right-clicking on any specific running process like you can terminate, stop or set the task priority.
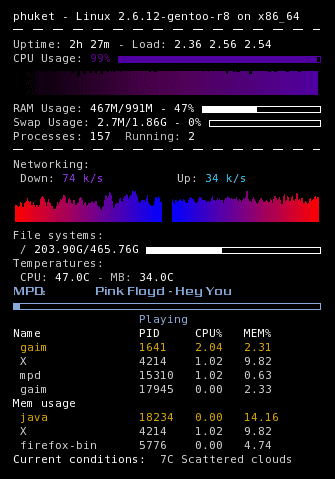
12. Conky
Conky is a free and cross-platform system monitor software for the X Window System. Users can install it on any Linux distro as it doesn’t depend on any specific Linux desktop environment. It shows important system information like system temperature, disk usage, CPU and memory usage, network resource stream, download and upload, system notifications, etc.
The Last Word
In this article, I have tried to focus on command-line and GUI-based monitoring tools. If you are an experienced and advanced Linux user, go for any CLI-based tool like “htop”; otherwise, go for GUI-based system tools to get your desired information.
Is this article on Linux Task Manager helpful? Did I miss including any other best Task manager for Linux here? If so, please let me know in the comment section. And don’t forget to share it on your social media. Leave any valuable suggestions in the comment below. Thanks.







