Hello, Linux enthusiasts. Today, I’ll be discussing some of the basic post-installation processes for Fedora Linux distributions. Note that these may vary depending on your chosen usage for the Fedora system. However, there are always a few key steps that most users should follow after a fresh installation, such as updating their repositories, enabling power-saving mode to improve battery life, and installing essential software applications.
Things To Do After Installing Fedora 37
 The following things should only be done if you have a reliable internet connection, as they all require data downloading from the server. With that being said, here are the best things to do for the post-Fedora installation.
The following things should only be done if you have a reliable internet connection, as they all require data downloading from the server. With that being said, here are the best things to do for the post-Fedora installation.
1. Setup DNF for Faster Packages Downloads
If you want your package downloads in Fedora to speed up, there are a few things you can do. By selecting the fastest mirrors, you can already see an improvement. If you have a fast internet connection, then another method is to change the number of parallel downloads in order to take advantage of that speed. You’ll just need to edit the DNF configuration files located at /etc/dnf/dnf.conf and make those changes happen.
To do this, open a terminal and type:
sudo nano /etc/dnf/dnf.conf
Append the following line and save:
max_parallel_downloads=10
2. Switch to a Faster dnf Mirror
Generally, the fastest mirrors are selected by those with the lowest latency. The speed difference might not always be detectable. If you want to increase your max_parallel_download, you can add two more lines as follows:
fastestmirror=true deltarpm=true
3. Update and Upgrade Your System
After you install a Linux distro, running updates is important to maintain the stability and security of your system. Fedora Linux, in particular, is known for its reliability, so it’s crucial that you update your packages regularly. Once per week should suffice to keep everything up-to-date. Use the below command in your terminal program to run an update:
sudo dnf check-update sudo dnf upgrade
4. Firmware Updates
You can check if your hardware manufacturer supports special firmware for Linux by running a quick sequence of commands. Even though it may not always be available, it is still worth trying.
sudo fwupdmgr refresh --force sudo fwupdmgr get-updates sudo fwupdmgr update
5. Enable RPM Fusion Repository
The Fedora installer has the option to include additional repositories from third-party sources. You will probably be prompted to do this in the Software Center as well. By default, only RPM repositories for NVIDIA drivers, Google Chrome, and Steam are included–which means that software such as VLC and MPV will not be available because it is typically found in RPM Fusion.
If you require additional tools that aren’t regularly accessible in the standard repositories or even in the filtered RPM fusion repo, it might be a beneficial idea for you to add the RPM Fusion repo. To enable both free and non-free versions of RPM Fusion on your system: Open up a terminal window and enter the following commands:
sudo dnf install https://download1.rpmfusion.org/free/fedora/rpmfusion-free-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpm sudo dnf install https://download1.rpmfusion.org/nonfree/fedora/rpmfusion-nonfree-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpm
Once you finish the above steps, enter the following code to update your system.
sudo dnf upgrade --refresh sudo dnf groupupdate core
6. Adding the Flathub Repository
Flatpak comes pre-enabled on Fedora, but if you want even more applications, you can add the Flathub repository via this command:
flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepo
7. Install Extension Manager App
The “Extensions” app is one of the essential Flathub apps. With it, you can easily search for, install and remove hundreds of GNOME extensions without having to visit the official website. To install Extensions, open a terminal and run:
flatpak install org.gnome.Extensions
8. Gnome Tweak Tool
The Gnome Tweak Tool is an essential application for Fedora installations. This program provides users with the ability to customize their desktop environment according to their own preferences. They can change themes, icons, fonts, colors, and user interface settings, to name a few features.
Simply run the command below to install the Gnome Tweak Tool on your computer:
sudo dnf install gnome-tweak-tool
9. Improve Battery Life and Reduce Overheating
Battery life and overheating are significant concerns for any device that uses a battery. Here, we have to take these into account when using Linux as well. TLP can be installed in order to reduce overheating and improve battery life almost immediately after installation is complete – no configuration required; simply install it, and you’re good to go! To install TLP, run the following command:
sudo dnf install tlp tlp-rdw
10. Install Multimedia Plugins
You need multimedia plugins on Fedora to play music, movies, and other audio or video files. Though you can install various media players, they all require additional media plugins or media codecs to function properly. To install the most common ones, run the following command.
sudo dnf install gstreamer1-plugins-{bad-\*,good-\*,base} gstreamer1-plugin-openh264 gstreamer1-libav --exclude=gstreamer1-plugins-bad-free-devel
sudo dnf install lame\* --exclude=lame-devel
sudo dnf group upgrade --with-optional Multimedia
11. Change the Device Name or Hostname
After installing Fedora Linux, the default device name is “Fedora.” If you want to change it to something more personal, there are two ways to do so. One is by using a terminal command, and the other is through Gnome settings in the About section.
Use the following command to change the Device name in Fedora Linux:
sudo hostnamectl set-hostname "New_Custom_Name"
12. Fedy Tool
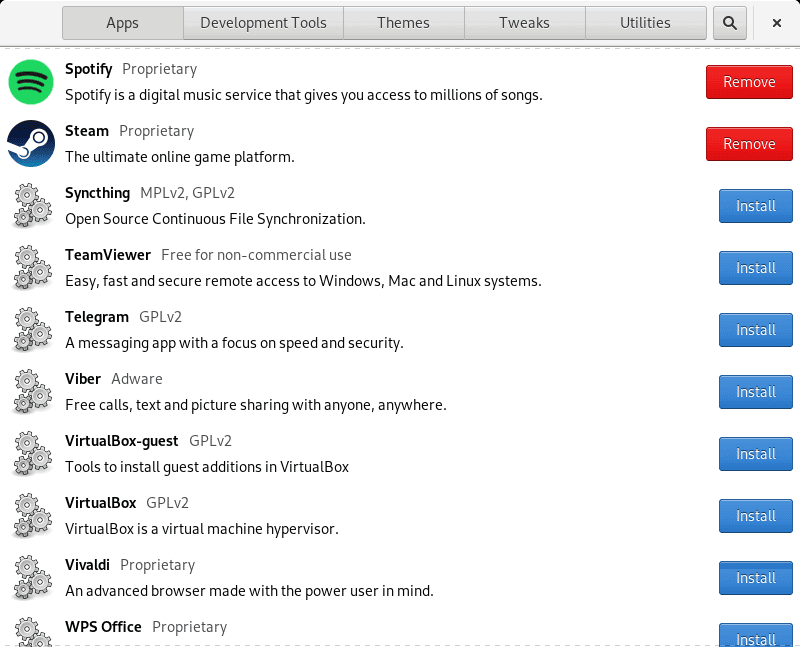 Now I recommend using the Fedy Tool to support mp3, Adobe Flash, Oracle Java, and more. With just one click, Fedy lets you install adobe flash player, Dropbox, Google Chrome, multimedia codecs, skype, WPS office, and other major apps.
Now I recommend using the Fedy Tool to support mp3, Adobe Flash, Oracle Java, and more. With just one click, Fedy lets you install adobe flash player, Dropbox, Google Chrome, multimedia codecs, skype, WPS office, and other major apps.
sudo dnf install https://download1.rpmfusion.org/free/fedora/rpmfusion-free-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpm https://download1.rpmfusion.org/nonfree/fedora/rpmfusion-nonfree-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpm sudo dnf copr enable kwizart/fedy sudo dnf install fedy -y
13. Install Some Best and Essential Applications
Fedora 37 workstation only comes with default applications, which are not enough to make the desktop functional. You can install additional software by using these commands, including office Suite, media player
sudo dnf install -y LibreOffice
sudo dnf install -y vlc
sudo dnf install -y transmission
sudo dnf install -y unzip p7zip p7zip-plugins unrar
sudo dnf install -y wine
sudo dnf install -y geary
sudo dnf install -y steam
sudo dnf install -y transmission
sudo dnf install -y dropbox nautilus-dropbox
14. Automatically Delete Trash Content
Automating the removal of files from your trash or bin is an important part of effective device storage management. But sometimes we forget to do that. To automate this process, you can set the following tweaks in your Fedora Linux system.
In order to toggle the Automatic Delete Trash Content and Temporary Files option, go to Settings → Privacy. The automatic deletion period is set to 30 days by default, but you can change it if you want.
15. Check Power Profiles
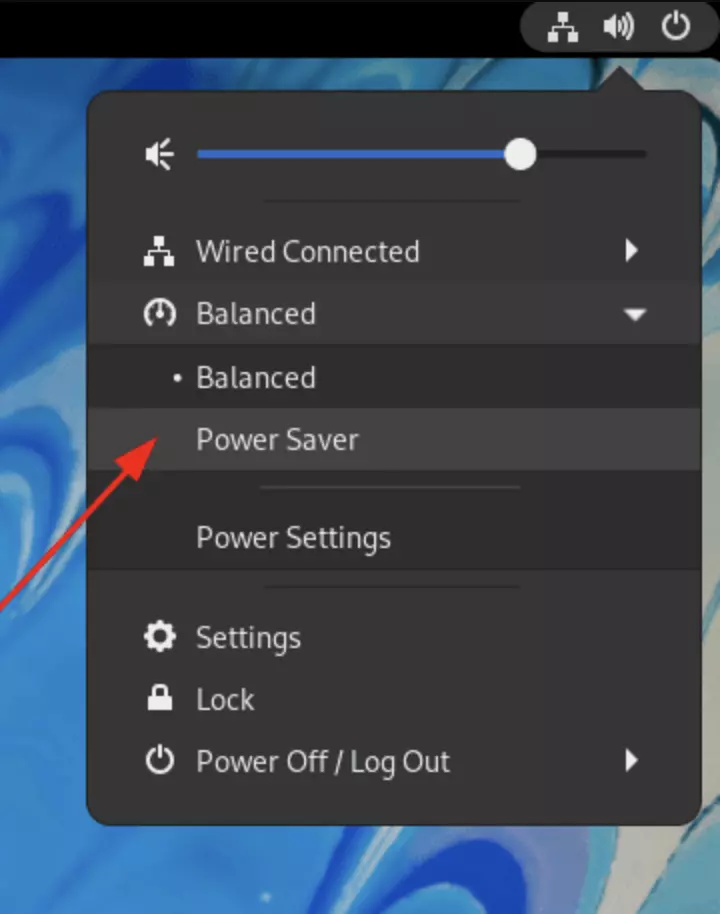 The Fedora 37 power profiles are located in the GNOME Control Center and Gnome user settings. If you want to save battery power, for example, on a laptop, choose “Power save” mode instead of normal mode. You can switch between modes from your user menu on the desktop whenever you need to.
The Fedora 37 power profiles are located in the GNOME Control Center and Gnome user settings. If you want to save battery power, for example, on a laptop, choose “Power save” mode instead of normal mode. You can switch between modes from your user menu on the desktop whenever you need to.
16. Get a VPN
A VPN is important for any system, Linux included. In 2023, every security agency will want to trace your online movements, which may not be something you’re okay with. Using a VPN is recommended for Linux systems.
There are various VPN providers that offer great features for a low monthly price. But which one should you choose? The answer may vary depending on your needs, but we’ve compiled a list of the best VPNs for Linux in 2023.
17. Install Themes and Icons
With Themes and Icons, we can transform the traditional desktop environment into something chic and trendy. If you’ve installed Gnome Tweak Tool already, it will be a breeze to install themes and icons onto your Fedora Gnome system. We have gone ahead and put together a list of the best Gnome themes and icons to help you make a selection for your own Fedora Gnome setup.
18. Install Different Desktop Environments
If you want to use a desktop environment other than the default Gnome in Fedora, follow the command below to install your desired DE. Fedora’s available desktop environments include KDE, XFCE, CINNAMON, MATE, and LXDE.
Please install each individual DE one at a time to avoid causing any damage or instability to your system. You should also know how to revert back before you install any specific DE just in case something goes wrong. This will save both your system and time in the long run.
- Install KDE Desktop
sudo dnf install @kde-desktop-environment
- Install MATE Desktop
sudo dnf install @mate-desktop-environment
- Install Cinnamon Desktop
sudo dnf install @cinnamon-desktop-environment
- Install XFCE Desktop
sudo dnf install @xfce-desktop-environment
- Install LXDE Desktop
sudo dnf install @lxde-desktop-environment
- Install LXQt Desktop Environment
sudo dnf install @lxqt-desktop-environment
- Sugar Desktop Environment
sudo dnf install @sugar-desktop-environment
- Install Deepin Desktop
sudo dnf install @deepin-desktop-environment
19. Enable Night Mode Using Redshift
The blue light from computers can have negative repercussions on our eyesight, so to lessen the impact, you can install this software. By running the following command in your terminal, you’ll be able to save your eyes from further strain.
sudo dnf install redshift
20. Install Nice-looking Fonts
The GNOME desktop’s default font on Fedora 37 is already great, but if you’re looking for something different, here are some cool fonts you can install. Once they’re installed, you can use the GNOME Tweak Tool to change them.
sudo dnf install -y 'google-roboto*' 'mozilla-fira*' fira-code-fonts
21. Change Touchpad settings
If you’re a laptop user, I recommend enabling the “Tap to Click” feature in your device settings. To do so, open Settings and go to Mouse & Touchpad. Then simply enable Tap to Click.
Finally, Insights!
Here is our list of things to do after installing Fedora 37. You should now be all set up and ready to use your new OS for daily tasks, depending on what you need it for. Just remember that Fedora (like any other distribution) is very configurable. If there’s something you don’t like about the system, feel free to change it until it better suits your needs!
I’ve tested all the Tips and Tricks mentioned above on the latest Fedora system and found no issues. However, be cautious when you’re installing it on your own device in case something goes wrong.
Did you try any of the tips listed above on your system? Or maybe you tried something completely different? Let us know about your experiences and suggestions in the comments section below. If you enjoyed this article, please share it with others to help us grow!
